
How long does Glutathione take to work: Science-Based Timeline
Posted in :
How Long Does Glutathione Take to Work? A Research-Based Timeline
Glutathione has been called the body’s master antioxidant for a reason. It’s involved in detoxification, immune balance, energy production, skin repair, inflammation control, and cellular protection. So it’s no surprise that many people turn to glutathione hoping for brighter skin, better immunity, or improved overall wellness.
But a common question always comes up:

How long does glutathione take to work?
The truth is this:
How fast you see results depends entirely on how you raise glutathione. Some methods work quickly but fade, while others build sustainable intracellular levels supported by decades of research.
Why Glutathione Timing Depends on the Method You Use
1. Glutathione Injections: Fast but Temporary
Glutathione IVs and injections deliver glutathione directly into the bloodstream, causing levels to rise quickly—often within hours.
You may notice:
- A temporary “glow”
- A short-lived brightening effect
- Mild detoxification sensations
- A small energy boost
However, the effects fade rapidly.
Glutathione’s half-life in the bloodstream is only 2–3 hours, and it does not consistently raise intracellular glutathione, which is where the body actually needs it for immunity, inflammation control, and skin repair.
2. Oral Glutathione Pills: Slow and Unpredictable
Many oral glutathione supplements break down before the body can use them. Liposomal forms improve this, but effects remain inconsistent.
Typical results:
4–8 weeks, with mild to moderate improvements.
3. Cysteine Precursors: The Most Effective and Most Sustainable
Your body needs cysteine to synthesize glutathione—but free cysteine is unstable.
Bonded cysteine, found in medically recognized whey protein isolates (like Immunocal), protects cysteine long enough for your cells to use it.
This is the only method clinically proven to raise intracellular glutathione.
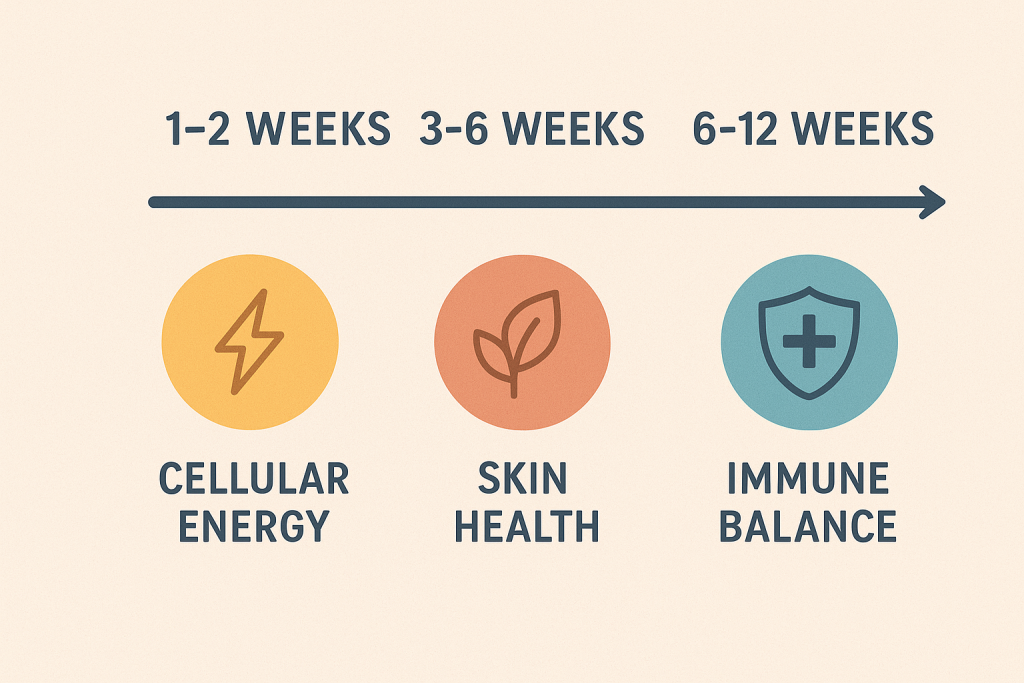
Timeline: What to Expect
Week 1–2:
- Energy improvement
- Decreased oxidative stress
- Better workout recovery
- Noticeable skin improvements
- More even tone and glow
- Improved inflammation balance
- Better immune resilience
- Greater cellular protection
- Deeper detoxification support
- Overall vitality
This timeline is supported by multiple clinical trials involving immune function and antioxidant status.
How Glutathione Interacts With Autoimmune Conditions
Autoimmune conditions often involve:
- High oxidative stress
- Low intracellular glutathione
- Imbalanced inflammatory responses
Glutathione is not a cure for autoimmune disease, but improving glutathione availability can help reduce oxidative load and support immune regulation.
Below is a seamless integration of evidence-based insights:
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
People with Hashimoto’s often show:
- Reduced glutathione peroxidase activity
- Higher oxidative stress in thyroid tissue
Supporting glutathione production may help the body buffer oxidative damage.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Research shows:
- Increased free radical presence
- Low intracellular glutathione levels
Enhancing glutathione synthesis may help protect joint tissue from oxidative injury.
Psoriasis
Psoriatic skin cells show:
- Disturbed redox signaling
- Excess oxidative stress
Internal glutathione support can promote healthier skin barrier function and cellular turnover.
Systemic Lupus (SLE)
SLE patients often have:
- Marked glutathione depletion
- Mitochondrial oxidative damage
Increasing endogenous glutathione may assist with cellular energy and resilience.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Studies highlight:
- Low glutathione in central nervous system tissue
- Elevated oxidative stress in neurons
Glutathione support may assist with neuroprotection and mitochondrial health.
Why Precursors Outperform Other Methods in Autoimmune Contexts
Autoimmune conditions tend to deplete glutathione rapidly.
Bonded cysteine precursors:
- Replenish glutathione inside cells
- Provide stable, consistent support
- Enhance detox, immune modulation, and mitochondrial function
- Build long-term resilience rather than quick fluctuations
This is why many clinicians emphasize precursor-based glutathione support instead of injections or pills.
So… How Long Does It Take to See Results? (Realistic Timelines)
Glutathione Injections
⏳ Hours to days
⚠️ Short-lived boost, not intracellular
Oral Glutathione
⏳ 4–8 weeks
⚠️ Absorption varies
Cysteine Precursors (Best Overall Option)
⏳ 1–2 weeks: energy + better recovery
⏳ 3–6 weeks: visible skin + inflammation support
⏳ 6–12 weeks: immune resilience + cellular repair
Final Takeaway
Glutathione is essential for skin health, immune balance, energy, and long-term cellular protection.
But if your goal is sustainable results, the method matters.
- Injections = quick but temporary
- Pills = inconsistent
- Cysteine precursors = scientifically validated, long-lasting intracellular glutathione support
This is the most effective way to support glowing skin, balanced immunity, and long-term wellness—especially for individuals managing autoimmune-related oxidative stress.

One thought on “How long does Glutathione take to work: Science-Based Timeline”